Search Results for: nuclear body
Nuclear body
Definition noun plural: nuclear bodies nu·cle·ar bod‧y, ˈnjuː.kli.ər ˈbɒdi Any of the prominent non-membraned,... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
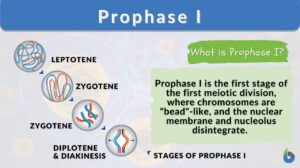
Prophase I
Organisms all use mitosis to create more cells in the body. Meiosis, a similar process, is used in some organisms to undergo... Read More
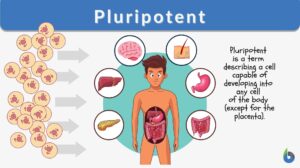
Pluripotent
Pluripotent Definition What is pluripotent? In biology, the term "pluripotent" means capable of developing into... Read More
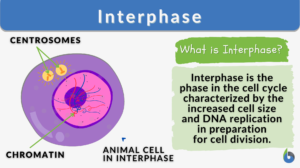
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Fragmentation
Fragmentation Definition What is fragmentation? In general, fragmentation refers to the state or the process of breaking... Read More
Dinoflagellate
A dinoflagellate is a flagellate algae characterized by their two flagella of unequal length. One of the flagella is lying... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
Spliceosome
spliceosome (Science: molecular biology) A complex of small nuclear organelles in which the splicing and excision reactions... Read More